Handout #2
The demand for labor will be less elastic
(1) the smaller the elasticity of substitution
(2) the smaller the elasticity of demand for the final product
(3) the smaller the initial ratio of labor costs to other costs, and
(4) the less elastic the supply of other factors
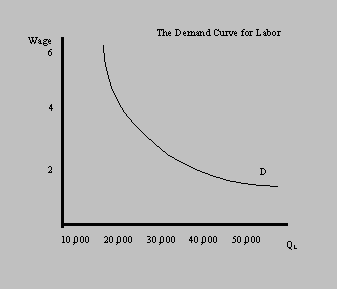
The demand curve represents the quantity of labor a firm is willing
to hire at given wage rates.

1. How much labor woule be hired at $3 per hour?
The demand curve can be described by the elasticity. The elasticity
of demand (Ed) is:
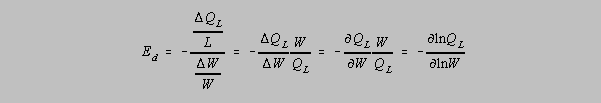 The elasticity of
demand describes how sensitive firms are in the quantity of labor they
demand, given changes in the wage rate.
The elasticity of
demand describes how sensitive firms are in the quantity of labor they
demand, given changes in the wage rate.
2. Compute the elasticity of demand assuming an initial wage of $2 per
hour that rises to $4 per hour.
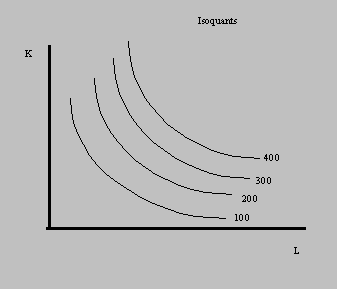
An isoquant represents all combinations of capital and labor that yield a given quantity of outputs.
The slope of an isoquant can easily be derived mathematically. Totally
differentiate Q:
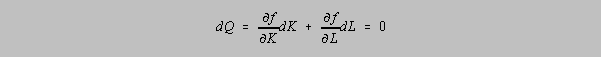 If output is held
constant than dQ=0. The slope of an isoquant is (dK/dL). Solving the above
equation implies:
If output is held
constant than dQ=0. The slope of an isoquant is (dK/dL). Solving the above
equation implies:
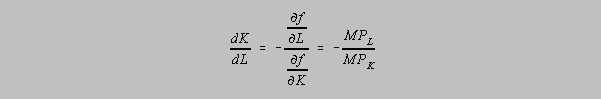
The curvature of the isoquant reflects the substitutability of K for
L (or L for K) in the production process. A measure of this curvature is
the elasticity of substitution denoted by .
An isoquant curve represents all combinations of capital and labor that
can be purchased for a given expenditure. Since total costs of production
can be expressed as:
![]() where
where
C = total cost
w = wage per unit of labor
r = rental rate for a unit of capital
K = capital
L = labor
then
![]() and the slope of
the isocost curve is:
and the slope of
the isocost curve is:
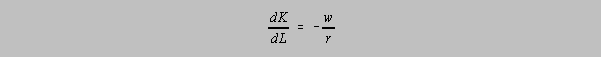 3. If Labor is $2
per hour and capital rents for $4 per hour, what is the slope of the isocost
curve?
3. If Labor is $2
per hour and capital rents for $4 per hour, what is the slope of the isocost
curve?
4. Draw the isocost curve if total expenditures are to be limited to
(a) $100, (b) $200, (c) $400. Which isocost curve is higher? Are they parallel?
Redo if the wage doubles from $2 per hour.
Qs = -200 + 200W -50R
where
Qs = quantity of labor supplied
W = wage rate
R = average rainfall per month
The demand for labor is given by:
QD = 1500-100W
where
QD = quantity of labor demanded
1. Do wet areas (ones with large amounts of rain) have higher or lower
wages than dry areas? (Explain using equations or a graph).
2. What will be the employment level in Reigns, Rhode Island (a city
with an average rainfall of 2 inches per minth)?
3. What would the unemployment rate in Reigns be if the minimum wage
were $8 per hour?